Enhance the lifetime of OLED by protecting from UV damage
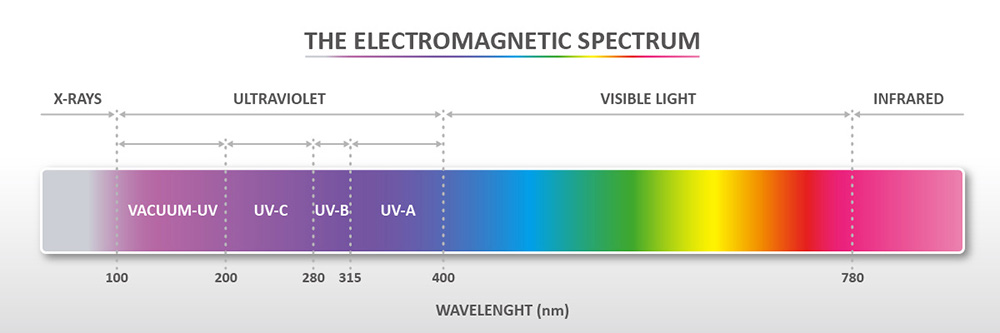
The Ultra-violet (UV) light has a shorter wavelength and greater energy (refer Figure 1) than visible light. If human beings expose to high-intensity UV light, it will lead to body damaged. Also, organic materials in OLED displays may be suffered by UV damage.
[Figure1 The electromagnetic spectrum]
It is common to use UV index to define the intensity of UV, which is an international standard measurement of the strength of the sunburn-producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. Please refer Chart.1
| UV index | Media graphic color | Risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure, for the average adult | Recommended protection |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 to 2 | Green | “Low” | A UV index reading of 0 to 2 means low danger from the Sun’s UV rays for the average person. Wear sunglasses on bright days. If you burn easily, cover up and use broad spectrum SPF 15+ sunscreen. Bright surfaces, sand, water, and snow, will increase UV exposure. |
| 3 to 5 | Yellow | “Moderate” | A UV index reading of 3 to 5 means moderate risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Stay in shade near midday when the Sun is strongest. If outdoors, wear sun-protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses. Generously apply broad spectrum SPF 15+ sunscreen every 1.5 hours, even on cloudy days, and after swimming or sweating. Bright surfaces, such as sand, water, and snow, will increase UV exposure. |
| 6 to 7 | Orange | “High” | A UV index reading of 6 to 7 means high risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Protection against skin and eye damage is needed. Reduce time in the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. If outdoors, seek shade and wear sun-protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses. Generously apply broad spectrum SPF 15+ sunscreen every 1.5 hours, even on cloudy days, and after swimming or sweating. Bright surfaces, such as sand, water, and snow, will increase UV exposure. |
| 8 to 10 | Red | “Very high” | A UV index reading of 8 to 10 means very high risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Take extra precautions because unprotected skin and eyes will be damaged and can burn quickly. Minimize sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. If outdoors, seek shade and wear sun-protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses. Generously apply broad spectrum SPF 15+ sunscreen every 1.5 hours, even on cloudy days, and after swimming or sweating. Bright surfaces, such as sand, water, and snow, will increase UV exposure. |
| 11+ | Violet | “Extreme” | A UV index reading of 11 or more means extreme risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Take all precautions because unprotected skin and eyes can burn in minutes. Try to avoid sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. If outdoors, seek shade and wear sun-protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses. Generously apply broad spectrum SPF 15+ sunscreen every 1.5 hours, even on cloudy days, and after swimming or sweating. Bright surfaces, such as sand, water, and snow, will increase UV exposure. |
[Chart.1 UV index]
The emitting layer made by organic material is the key factor behind the light emission of OLED displays. High-intensity energy will damage the structure of organic material in the emissive layer, which causes low light-emitting efficiency and fast brightness decay.
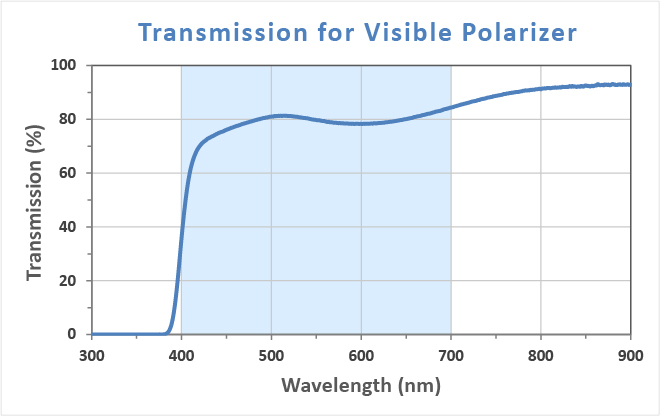
In order to protect the organic material from UV damage, we have to minimize the intensity of UV wavelength. Meanwhile, we don’t want to decrease the intensity in the visible light range(400nm~700nm). For this purpose, add a polarizer which the transmission of wavelength < 380 um (UV band) is under 1% is a very suitable solution. Please refer Figure.2.
[Figure.2 transmission spectrum of polarizer]
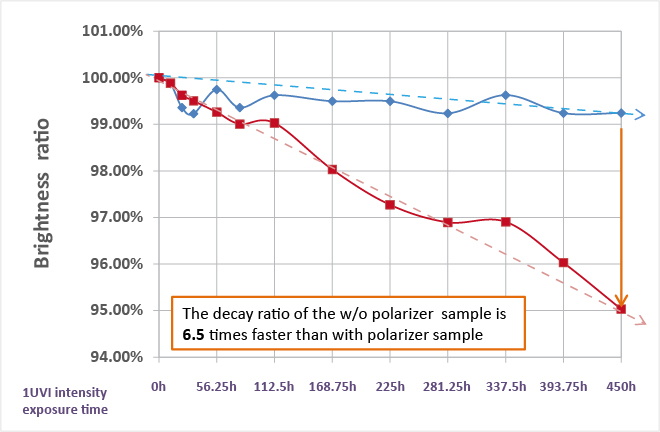
We designed an experiment to find out the polarizer’s ability of UV protection. We covered the half area of the OLED panel with polarizer, and the remaining area was not covered. Then we put the OLED panel into a UV chamber and measured the brightness decay rate for both areas. Please check the Figure.3. After suffering energy equaling to 1 UVI intensity expose 450 hours, the decay rate of the area covered by the polarizer ( blue line) is 0.76%, and the decay rate of area without any cover (red line) decayed 4.97%. It shows the polarizer can protect the organic material from UV damage.
[Figure.3 The curve of OLED brightness decay with (blue line) and without (red line) polarizer covered]
In summary, OLED modules with polarizer can resist the damage of UV exposure effectively. It is recommended that the products which might be exposed to the sun should add polarizer to protect the OLED panel. Generally, there is no issue for handheld products with polarizer used in outdoor application. For outdoor fixed-position devices, it is recommended the modules should add a polarizer and a shed to avoid long-term direct sunlight to extend the OLED lifetime.